Kitchen wastewater treatment system project case
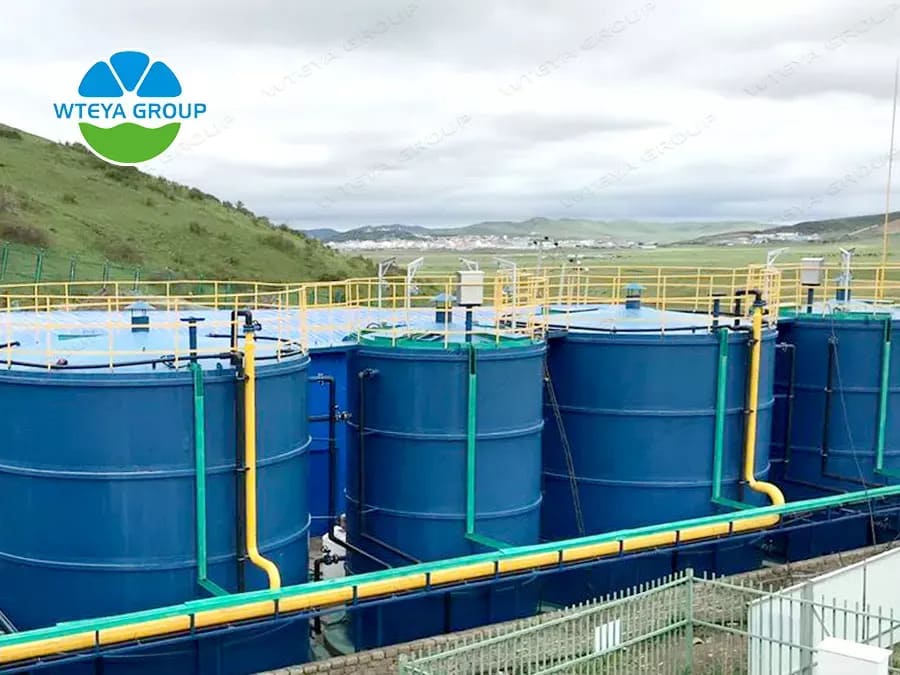
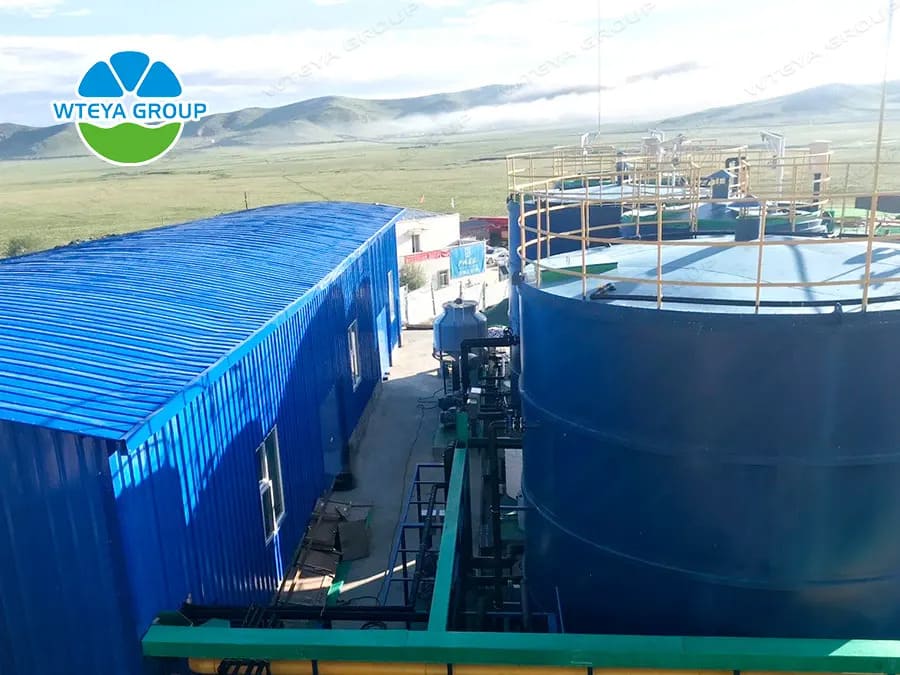


Basic information about the project
Project name: Ruoergi County domestic waste leachate disposal upgrade project
Project address: Ruoergi County, Aba Prefecture, Sichuan Province
Treatment scale: kitchen wastewater, incineration power plant leachate, landfill leachate mixed wastewater, water intake of 30T/D
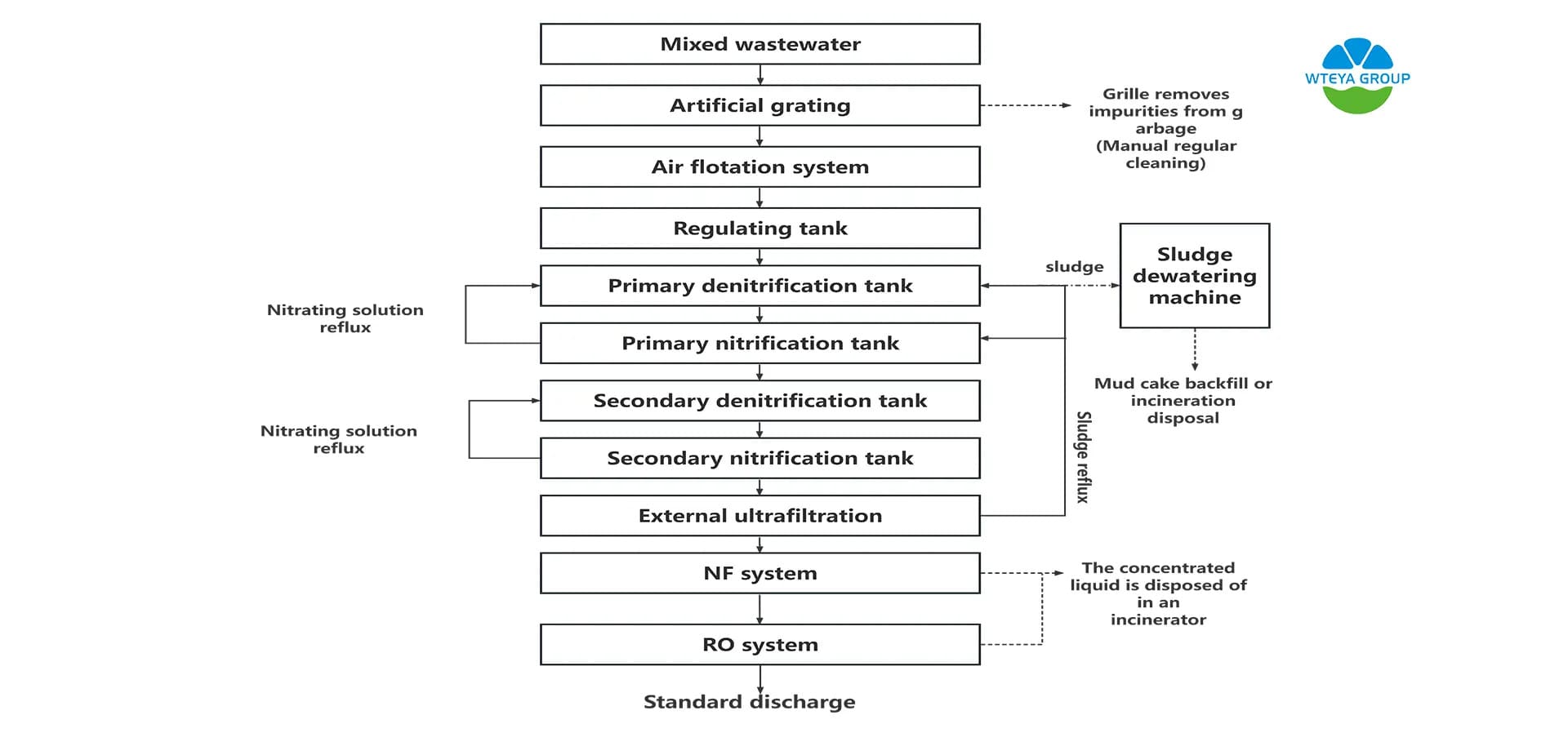
1. Two-stage nitrification and denitrification process
After the A/O process, the addition of A two-stage anoxic reactor (A pool) and A fast aerobic reactor (0 pool) is A two-stage A/0 process, the second stage A/0 is mainly used for the removal of residual nitrate and nitrogen and the excessive addition of organic matter in the secondary A pool, which also makes the process have a stronger impact load resistance. The two-stage A cell solves the problem of limited nitrogen removal capacity of A/0 process. However, the end 0 tank makes it difficult for denitrification to occur in the secondary sedimentation tank and N2 is produced to make the sludge float up.
Process features:
- The process is simple, no additional carbon source and post-aeration tank is required, the original sewage is used as the carbon source, and the construction and operation cost is low;
- Before denitrification, after nitrification, set up an internal cycle, using the organic substrate in the original sewage as the carbon source, the effect is good, and the denitrification reaction is sufficient;
- After the aeration tank, the denitrification residue can be further removed and the quality of the treated water can be improved;
- Stirring in stage A will only suspend the sludge and avoid an increase in DO. Strong aeration is adopted in the first part of section O, and the gas volume is reduced in the latter part to reduce the DO content of the inner circulating liquid, so as to ensure the anoxic state of section A.

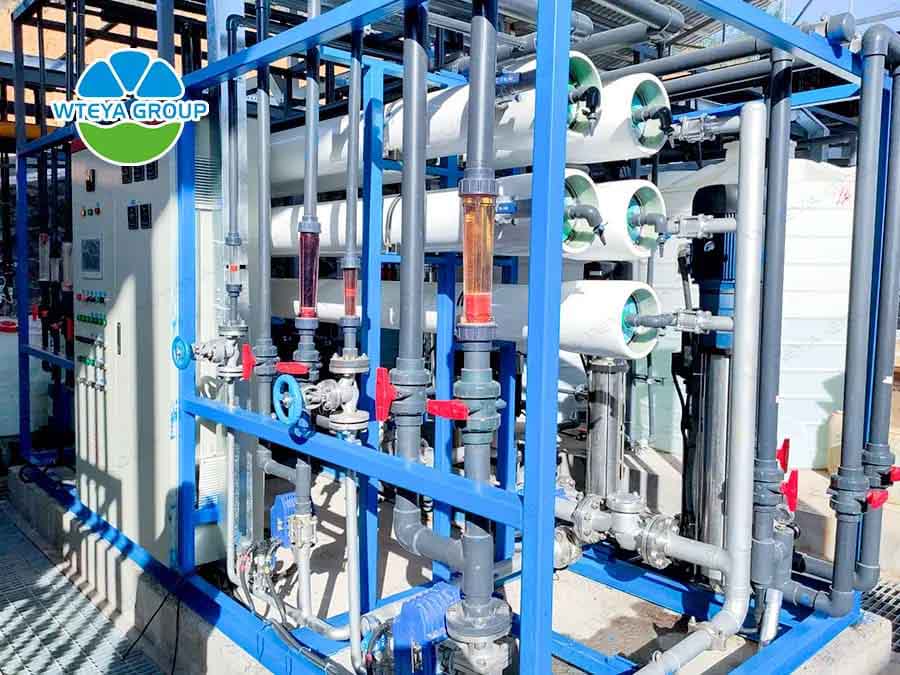
2. tube ultrafiltration process
Ultrafiltration membrane is one of the membrane separation technology, its interception aperture is 0.1-0.01 micron, can be suspended matter, microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, etc.), colloid completely interception, while can intercept part of macromolecular organic matter, is an efficient and environmentally friendly separation process, compared with traditional separation technology such as distillation, adsorption, absorption, extraction, cryogenic separation, etc. It has many advantages.
- Independent operation, easy control, low labor cost;
- High flux, generally 50-120L/(m2.h), which is 6-10 times that of ordinary immersion;
- No recoil, easy to clean;
- No concentrated water discharge, water recovery rate can reach 100%;
- Easy to replace, can be replaced by a single branch;
- reliable operation, general life of 5 years;
- Tubular membrane has greater advantages than other membranes mainly in: The sludge concentration of the MBR pool can reach up to 40g/L, and the other membrane groups are 10g/L, so the biochemical pool covers only about 1/3-1/4 of the other membranes, the infrastructure investment is less, the tubular membrane has a long service life and the quality guarantee period is 5 years, and the other membranes are about 3 years. The tubular membrane can be installed on the surface (the installation method is the same as nanofiltration and reverse osmosis, which is easy to manage). There are no problems such as broken or damaged wires of other membranes, convenient operation and management, online cleaning, small operation and operation workload, other membranes (such as flat membranes, window membranes, etc.) need to be located in the biochemical tank easy to break wires, chemical cleaning needs to be set up to move out of the pool for cleaning and other factors, and tubular membranes are easy to clean, not easy to block, the actual comprehensive cost of using tubular membranes is saved compared with other membranes.
3. nanofiltration process
Nanofiltration membrane: Pore size above 1nm, generally 1-2nm is a functional semi-permeable membrane that allows solvent molecules or some low molecular weight solutes or low-cost ions to pass through. It is a special and very promising variety of separation membrane, it is named for the size of the substance can be intercepted about nanometers, it intercepts the molecular weight of organic matter is about 150-500, the ability to intercept dissolved salt is between 2-98%, the univalent anionic salt solution is lower than the high anionic salt solution. It is used to remove organic matter and chroma from surface water, remove hardness from groundwater, partially remove dissolved salts, concentrate fruit juices, and separate useful substances in pharmaceuticals.
Process features:
- The concentration and purification process is carried out at room temperature, no phase change, no chemical reaction, no other impurities and the decomposition and denaturation of the product, especially suitable for heat-sensitive substances.
- Can remove the salt of the product, reduce the ash content of the product, improve the purity of the product, compared with solvent desalination, not only the product quality is better, and the yield can also be improved.
- High yield and less loss in the process.
- Acid, alkali, alcohol and other effective substances can be recovered in the solution to achieve the recycling of resources.
- Equipment structure is compact, small footprint, low energy consumption.
- Easy to operate, can achieve automatic operation, good stability, easy maintenance.
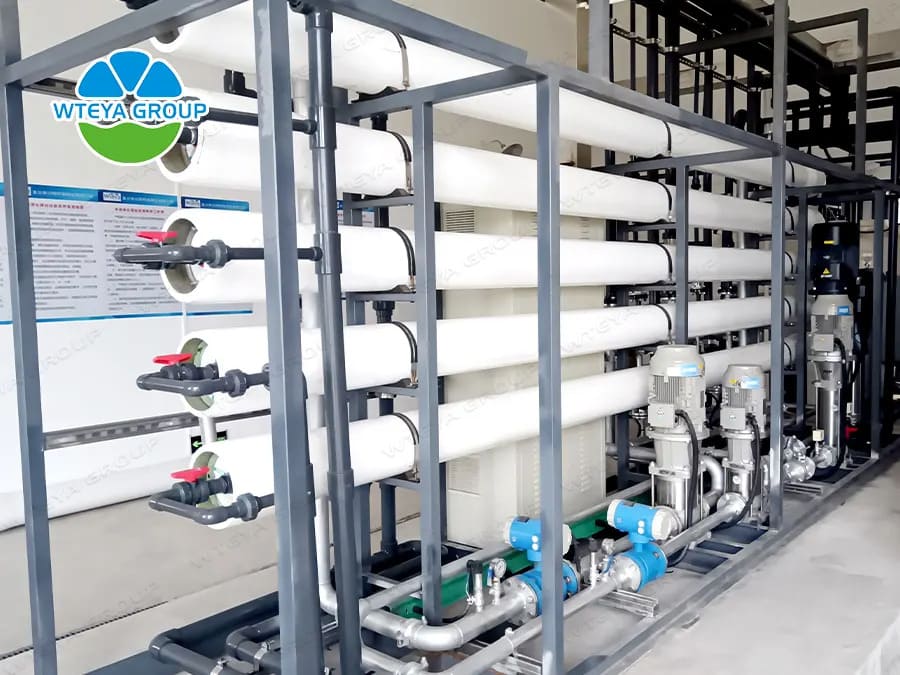

4. reverse osmosis process
RO membrane aperture is one millionth of the hair (0.0001 micron), generally can not be seen by the naked eye, bacteria, viruses are 5000 times its, therefore, only water molecules and some mineral ions can pass (through the ions are not beneficial to damage orientation), other impurities and heavy metals are discharged by the wastewater pipe.
Reverse osmosis membrane is the core element of reverse osmosis. It is a kind of artificial semi-permeable membrane made by simulating biological semi-permeable membrane. Generally made of polymer materials. Such as cellulose acetate membrane, aromatic polyacyl callosal membrane, aromatic polyamide membrane. The diameter of the surface micropores is generally between 0.5 and 10nm, and the size of the permeability is related to the chemical structure of the film itself. Some polymer materials have good repulsion to salt, and the penetration rate of water is not good. The chemical structure of some polymer materials has more hydrophilic groups, so the water penetration rate is relatively fast.
Process features:
- the effluent stable standard, not affected by the raw water quality
- operation flexibility and impact resistance
- the lowest degree of membrane scaling and contamination
- long service life of the film
- Membrane components are easy to maintain
- low investment and operating costs
- high degree of automation, easy to operate











